MIL-DTL-917F(SH)
3.2.24.1 Fastening of parts. Except for motors, generators, and motor generators, through bolting shall be used
wherever practicable as specified (see 6.2). For electrical panels and other applications where frequent disassembly
is required, blind nuts and captive fasteners shall be used when practical. The preferred blind nuts are blind rivet
nuts, blind threaded inserts, and insert nuts when frequent removal for maintenance and repair is required.
Self-clinching fasteners and clinch nuts are not preferred and can only be used in cases where disassembly is never
required for maintenance and repair. Similarly, these types of fasteners shall be used when practical to prevent a
loose fastener from dropping into electrical equipment.
3.2.24.2 Fitted bolts. The holes for fitted (also known as body-bound) bolts shall be reamed with the coupled
parts in position and chamfered. Where practicable, the shank of the bolt shall have definite interference with the
metal surrounding the hole. The mating surfaces of the bolt and hole shall have a smoothness of 63 micro-inches
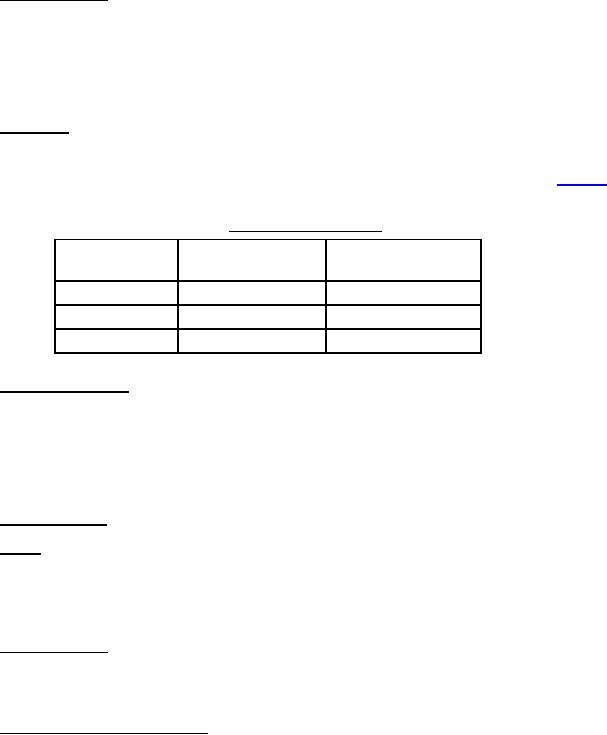
roughness height rating (RHR) or smoother in accordance with ASME B46.1. Bolt-to-hole fit is shown in table IV.
TABLE IV. Bolt and hole dimensions.
Nominal size
Max. clearance (+)
Max. interference (-)
(inches)
diameter (inches)
diameter (inches)
½ to 1¼
0.0005
0.0010
1¼ to 1⅞
0.0006
0.0013
2 to 3
0.0007
0.0016
3.2.24.3 Threads in aluminum. Threads in aluminum or aluminum alloys shall be avoided, where practicable,
by use of through bolting. Where through bolting is not practicable, and screws must be removed for routine
equipment maintenance or where high stress in the screw is required for alignment of a vital part, metal inserts for
the fastenings shall be cast or screwed into the aluminum or aluminum alloy. Inserts shall be given a
corrosion-resistant treatment, except where bushing type inserts of corrosion-resistant steel are cast into the
aluminum or aluminum alloy. Inserts need not be provided for securing identification plates, terminal boards, or
other items that are removed only when the equipment is overhauled or modified.
3.2.24.4 Threads in plastic. Metal inserts shall be used where threads in plastic are required.
3.2.24.5 Inserts. Metal inserts, where required in aluminum alloys or plastics, shall be the bushing type or the
helical-coil type conforming to NASM21209. Refer to MS21208 for additional guidance. The bushing type is
recommended. The use of helical-coil type inserts shall be limited to applications where the threaded hole permits
full engagement of the insert. Bushing type inserts shall be the cast-in, molded-in, or screwed-in types. Screwed-in
types shall be pin-, key-, swage-, or ring-locked to prevent backing out (see 3.16.6).
3.2.24.6 Thread projection. Except for threading into blind holes or in thick material, bolts and machine screws
shall be of such length that when tightened, at least one thread and preferably not more than four threads shall
project beyond the outer face of the nut or bolted part. With plastic insert self-locking nuts, the thread projection
shall be measured from the crown of the plastic insert.
3.2.24.7 Bolt and screw thread engagement. Minimum thread engagement for tapped holes and threaded
inserts is as follows:
a. Minimum thread engagement for tapped holes is whichever is longer: (1) the fastener major (nominal)
diameter plus one thread or (2) as calculated per the Design of Unified Scew Threads Appendix of FED-STD-H28/2
plus one thread.
b. Where threaded inserts are used (see 3.2.24.5 for limitations), the length of the thread engagement shall be
not less than 1½ times the fastener major (nominal) diameter.
24
For Parts Inquires submit RFQ to Parts Hangar, Inc.
© Copyright 2015 Integrated Publishing, Inc.
A Service Disabled Veteran Owned Small Business